New Hampshire letter on substandard & discriminatory HIV medication coverage & plan design by Harvard Pilgrim Health Care

Commissioner
State of New Hampshire Insurance Department
21 South Fruit Street, Suite 14
Concord, NH 03301
Dear Commissioner Bettencourt:
The HIV+Hepatitis Policy Institute is writing to express our concern about substandard, discriminatory coverage of HIV treatment medications by Harvard Pilgrim Health Care health plans that use its 2025 “Core 4 Tier” and “Core 5 Tier” formularies in New Hampshire.
These plans do not meet the regulatory standards for formulary adequacy in CFR 156.122 (a)(3)(iii)(H) by failing to cover treatment regimens recommended in broadly accepted treatment guidelines and that are indicative of clinical best practice, thereby discouraging enrollment by people living with HIV.[1]
We urge the New Hampshire Insurance Department (NHID), which reviews, approves, and regulates individual, small group, and fully-insured large group plans in New Hampshire, to take immediate action against Harvard Pilgrim Health Care for offering these substandard and discriminatory plans that violate the ACA and its implementing regulations. Since this will immediately impact the treatment of people living with HIV who are currently on these plans and they require continuity of their treatment, we urge you to ensure that these violations are rectified quickly before these formulary changes go into effect on January 1, 2025. [2]
Harvard Pilgrim Health Care’s New Hampshire Core 4-Tier and 5-Tier Formularies Fail to Reflect HIV Treatment Guidelines and Clinical Best Practice
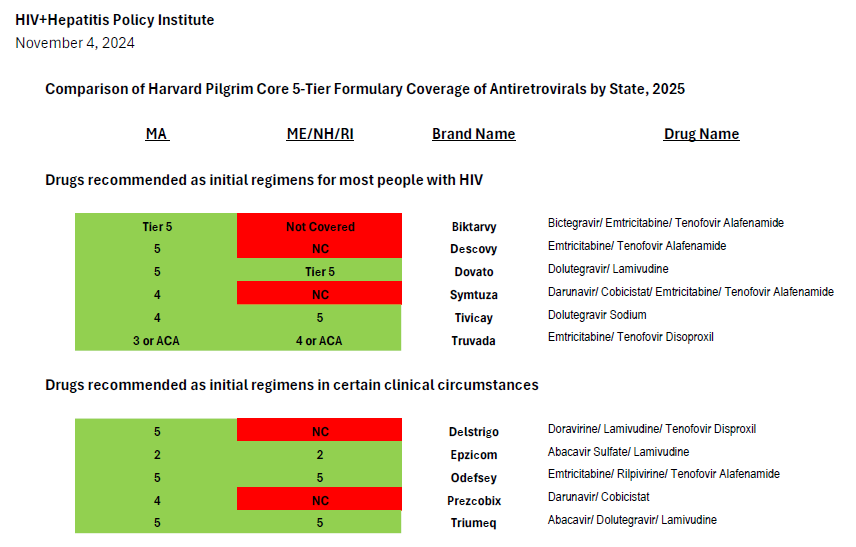
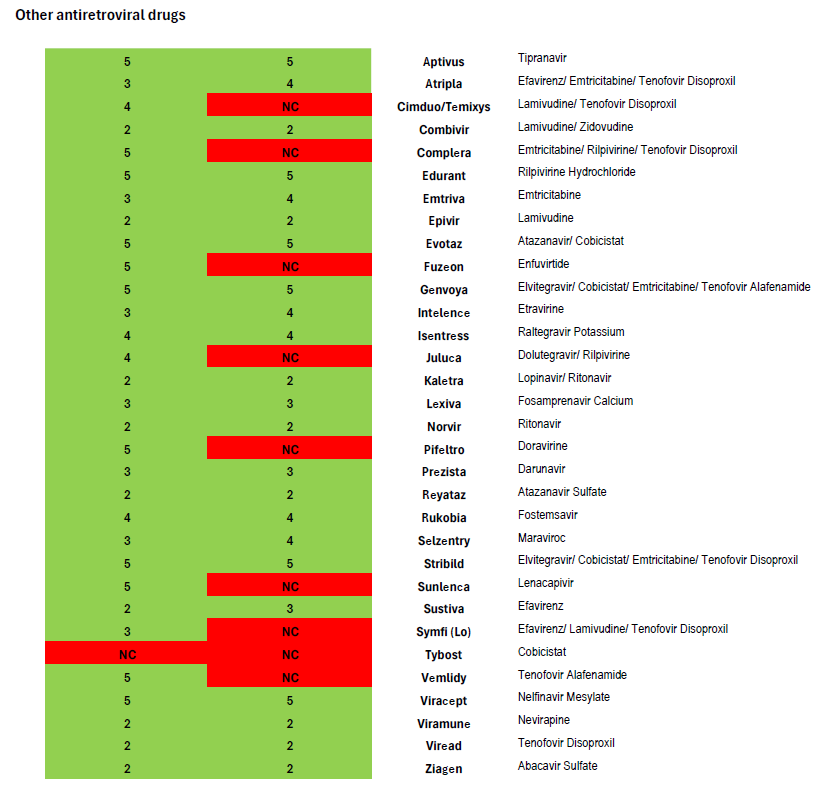
After comparing Harvard Pilgrim’s coverage of antiretroviral drugs in its New Hampshire Core 4- and 5-Tier formularies[3] with the United States Department of Health and Human Services Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents with HIV, we find it impossible to conclude that the insurer is in compliance with the regulation and that clinically-based reviews were adequately completed.[4] Coverage of antiretrovirals is summarized in the chart attached.
Current guidelines recommend four preferred regimens as initial therapy for most people (Biktarvy, Dovato, Symtuza, or a combination of Tivicay with either Truvada or Descovy).[5] These plans only cover two, Dovato or Tivicay + Truvada – one of which is only partially covered.[6] The recommended regimens are preferred due to their “demonstrated durable virologic efficacy, favorable tolerability and toxicity profiles, and ease of use.” Biktarvy is the most commonly prescribed treatment regimen in the United States and is currently prescribed to over 49 percent of people with HIV.[7] Though the combination of Tivicay + Truvada is covered, the combination of Tivicay + Descovy is increasingly required for many due to the greater kidney and bone toxicities associated with Truvada compared to Descovy. This is especially an issue since the median age of people living with HIV in the United States is 51 and continues to rise.
Symtuza is the only recommended initial regimen for individuals who have taken the new long-acting injectable PrEP medication Apretude (cabotegravir) but are starting antiretroviral therapy before results of resistance testing are available. Covering only two out of four preferred initial regimens—with one of the two covered regimens not covered fully – is not sufficient coverage.
Current guidelines recommend four alternative regimens as initial therapy in certain clinical circumstances (Delstrigo, Odefsey, Triumeq, and a combination of Prezcobix and Epzicom). Of these, only two (Odefsey and Triumeq) are covered, continuing the pattern of inadequate coverage.
The eight preferred and alternative regimens we have described above are only the broadest of the recommendations made in the national treatment guidelines. The complexity of HIV treatment is reflected in the detailed recommendations made in national guidelines for specific populations, such as pediatric patients, pregnant individuals, or people experiencing ongoing HIV viremia.
Clinicians weigh many factors as they consider which treatment regimen best suits the needs of their patients, including the many significant comorbidities that impinge on HIV treatment and the consequences of the development of different resistant strains of HIV. Clinicians are careful to prescribe a combination of antiviral drugs that will continue to leave options for people who have developed resistance mutations that leave the patient unable to take certain drugs or classes of drugs.
Heavily treatment-experienced people living with HIV may have few options to construct a fully virally suppressive regimen. As the national treatment guidelines note, such individuals may be candidates for antiretroviral drugs which are the first-in-class, such as the new long-acting medication Sunlenca (lenacapavir)—another drug not covered in Harvard Pilgrim’s 2025 Core 5-Tier formulary.
In contrast, Harvard Pilgrim’s equivalent Core 5-Tier formulary used for 2025 plans in Massachusetts covers all eight of the preferred and alternative regimens in national treatment guidelines (as illustrated in the attached formulary review.) The Massachusetts plan also covers Sunlenca, along with nearly all antiretroviral drugs other than old or rarely used medications. This demonstrates that Harvard Pilgrim is well-aware of the treatment guidelines and able to provide non-discriminatory coverage that follows clinical recommendations.
Since most people with HIV enrolled in Harvard Pilgrim Marketplace plans in New Hampshire are currently on a drug regimen that will no longer be covered, they will encounter serious treatment interruptions in the new plan year. Some will be forced to switch plans, clearly demonstrating how these substandard plans discourage enrollment by people with HIV. This is dangerous for their individual health, public health, and for communities disproportionately impacted by HIV.
This also imposes additional burdens on their clinical providers, who might be forced to prescribe an alternative medication—for no good clinical reason. HIV/AIDS service organizations and community-based organizations serving people living with HIV will all struggle to support patients experiencing access problems. Harvard Pilgrim individual market plans are a preferred option for enrollees of the New Hampshire AIDS Drug Assistance Program (ADAP) due to in-network access to Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, the state’s only academic medical center and a key provider of HIV care in the state. According to its website, New Hampshire ADAP “pays fully for a client’s medicines when a primary insurer denies payment for a prescribed medicine,” meaning that the program and the low-income clients it serves will be heavily impacted by the consequences of this discriminatory formulary.
We urge NHID to take immediate action to bring Harvard Pilgrim coverage in line with HIV treatment guidelines and into compliance with all ACA coverage requirements.
We look forward to learning what actions you have taken or will take with regard to Harvard Pilgrim’s Core 4- and 5-Tier formularies and to ensure that all state-regulated plans in New Hampshire meet ACA requirements for non-discriminatory coverage of HIV treatment.
If you have any questions, comments, or would like to discuss these issues further, please contact Carl Schmid, Executive Director, HIV+Hepatitis Policy Institute at cschmid@hivhep.org or (202) 462-3042, or Kevin Herwig, Health Policy Manager, HIV+Hepatitis Policy Institute at kherwig@hivhep.org or (617) 666-6634.
Sincerely,

Carl E. Schmid, II
Executive Director
cc: Ellen Montz, Director, CCIIO
Jeff Wu, Deputy Director for Policy, CCIIO
Melanie Fontes Raine, Director, HHS Office for Civil Rights
Dr. Laura Cheever, Associate Administrator, HIV/AIDS Bureau, HRSA
Francisco Ruiz, Director, White House Office of National AIDS Policy
[1] https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-45/subtitle-A/subchapter-B/part-156/subpart-B/section-156.122
[2] A similar formulary is used in Rhode Island and Maine. We are also submitting formal complaints to insurance regulators in those states.
[3] We have not conducted an exhaustive review of all formularies Harvard Pilgrim may offer in the individual, small group, and fully-insured large group markets. We urge NHID to review all formularies for discriminatory coverage.
[4] https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/guidelines
[5] https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/adult-adolescent-arv/tables-adult-adolescent-arv.pdf (Table 6a)
[6] Coverage of Cimduo could also substitute for coverage of Truvada.
[7] https://s29.q4cdn.com/585078350/files/doc_financials/2024/q2/GILD-Q224-Earnings-Presentation-8-August-2024.pdf